
Mental health disorders are conditions that affect your mood, thinking, and behavior. They are more common than many people realize and can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the different types of mental health disorders, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing these conditions effectively.

Anxiety disorders are the most common type of Mental Health Disorders. People with these conditions experience severe fear or anxiety related to certain objects or situations. They often try to avoid exposure to whatever triggers their anxiety. Examples include Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, and various phobias.
Mood disorders involve disturbances in a person’s mood, leading to periods of intense sadness or overly happy states. Common mood disorders include Depression and Bipolar Disorder. These conditions can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being.
Psychotic disorders involve distorted thinking and awareness. Schizophrenia is a well-known psychotic disorder where individuals may experience delusions, hallucinations, and other cognitive difficulties. These symptoms can make it hard to distinguish between what is real and what is not.
Understanding Mental Health Disorders is crucial for recognizing and addressing these conditions effectively. There are many different types of mental illnesses that range in severity.

Emotional symptoms can vary widely but often include feeling sad or down, experiencing excessive fears or worries, and having extreme mood changes. Persistent feelings of hopelessness and low energy are also common. People may also feel detached from reality, experiencing delusions or hallucinations.
Behavioral symptoms might include withdrawing from friends, family, and activities you once enjoyed. You may notice changes in eating or sleeping habits, such as eating too much or too little, or sleeping too much or too little. Other signs include using mood-altering substances more frequently and having trouble completing daily tasks like getting to work or cooking a meal.
Sometimes, mental health disorders show up as physical problems. These can include unexplained aches and pains, such as stomach pain, back pain, or headaches. Changes in your sex drive and significant tiredness are also common physical symptoms. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to seek help.
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a big difference in managing mental health disorders effectively.
Mental illnesses often run in families, suggesting that genetic factors play a role. If a close relative has a mental health disorder, your risk might be higher. However, having a family history doesn’t guarantee you will develop a condition.
Your surroundings can greatly impact your mental health. Stressful life events like losing a loved one, financial problems, or living in a high-crime area can increase the risk. Childhood adversity, such as abuse or neglect, also plays a significant role.
Biological factors include brain chemistry and physical health conditions. Imbalances in neurotransmitters can lead to disorders like depression. Chronic illnesses such as diabetes or cancer can also contribute to mental health issues.
It’s important to note that mental well-being depends on a balance of factors, and several elements may contribute to the development of a mental health disorder.
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing a mental illness:
Understanding these risk factors can help in identifying and managing mental health disorders early on.

To start, doctors will look at your medical history and do a physical exam. This helps them rule out any physical problems that might be causing your symptoms. They might also order lab tests, like checking your thyroid or screening for alcohol and drugs.
Next, a mental health professional will talk to you about your symptoms, thoughts, and feelings. You might fill out a questionnaire to help them understand your behavior patterns. This step is crucial for getting a clear picture of what you’re going through.
Finally, doctors use a manual called the DSM-5 to diagnose mental health disorders. This book lists the symptoms for each disorder and helps doctors figure out which one you might have. Getting the right diagnosis is important for finding the best treatment for you.
Taking the time to get an accurate diagnosis can make a big difference in your treatment plan.

Medication can be a key part of treating mental health disorders. Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and anti-anxiety medications are commonly prescribed. These drugs help balance chemicals in the brain, reducing symptoms and improving daily life. It’s important to take medication exactly as prescribed and to discuss any side effects with your doctor.
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, involves speaking with a mental health professional to address emotional and psychological issues. Common types include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and dialectical behavior therapy. These therapies can help individuals understand the root causes of their conditions and develop coping strategies.
Alternative therapies can also be beneficial. These might include herbal remedies, acupuncture, yoga, and meditation. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatment to ensure it won’t interfere with other medications or treatments.
Combining different treatment options can often lead to better outcomes. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to find the best plan for your needs.

Making lifestyle changes can greatly improve mental health. Some helpful changes include:
A strong support network is crucial. This can include self-help groups or close friends and family. Connecting with others who understand your struggles can provide emotional relief and practical advice.
Developing effective coping mechanisms is essential for managing mental health. Some strategies include:
Building a support network and making lifestyle changes can significantly improve mental well-being. It’s important to find what works best for you and stick with it.
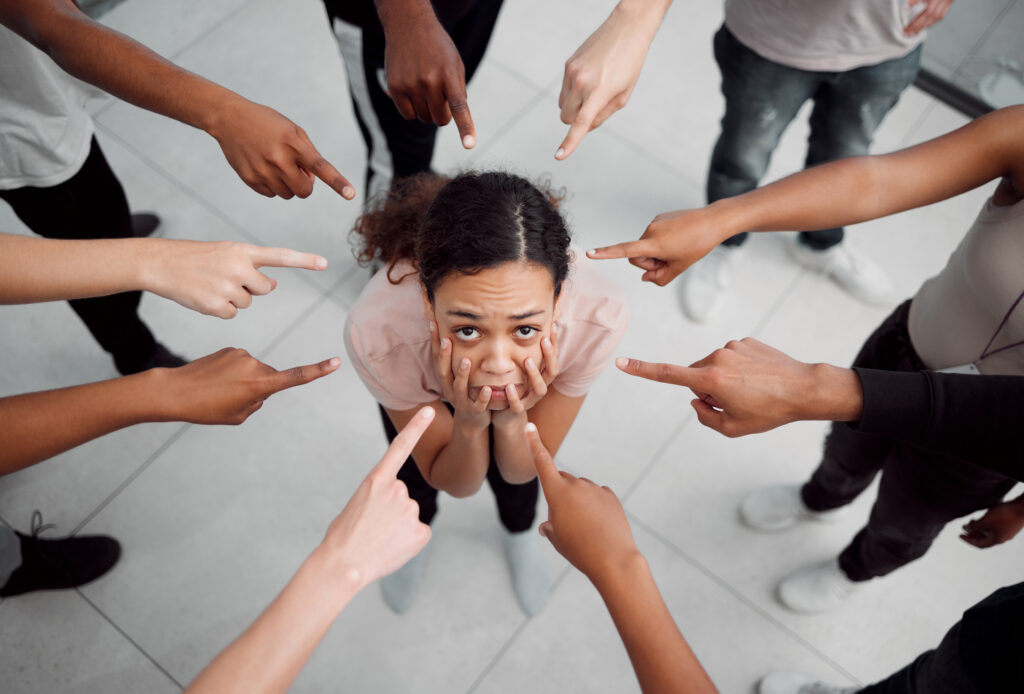

Stigma around mental health can make people feel ashamed or embarrassed. This often stops them from getting the help they need. Stigma can lead to isolation and make recovery harder. It’s important to know that mental health issues are common and nothing to be ashamed of.
Talking openly about mental health can help break down stigma. Here are some ways to encourage open conversations:
Seeking professional help is a big step towards recovery. Here are some tips to find the right help:
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. You deserve support and care.
Facing stigma can be tough, but getting help shouldn’t be. At AM Health Care, we offer a range of programs to support you or your loved one. Don’t wait—take the first step towards recovery today. Visit our website to learn more about our services and how we can assist you.
Understanding mental health disorders is crucial for everyone. These conditions can affect anyone, regardless of age, background, or lifestyle. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking help can make a big difference. Treatments like therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can help manage these disorders. Remember, it’s okay to ask for help. Taking care of your mental health is just as important as taking care of your physical health. Let’s work together to break the stigma and support each other on this journey to better mental health.
Some common types of mental health disorders include anxiety disorders, mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder, and psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
Symptoms can vary but often include emotional signs like feeling very sad or worried, behavioral changes like withdrawing from friends, and physical symptoms such as tiredness or trouble sleeping.
Mental health disorders can be caused by a mix of genetic, environmental, and biological factors. Stressful life events, family history, and brain chemistry can all play a role.
Doctors use a combination of medical history, physical exams, and psychological evaluations. They may also use diagnostic criteria from manuals like the DSM-5.
Treatment can include medication, psychotherapy (talk therapy), and alternative therapies like yoga or meditation. Often, a combination of treatments works best.
You can support them by encouraging open conversations, being patient, and helping them find professional help. Joining support groups and learning more about their condition can also be beneficial.
